class 7 Time and motion
Class 7
Time and Motion (Physics)
Questions covered are:
1. What are time measuring devices in ancient times?
2. What are natural events our ancestors used to measure time?
3. Measurement of Time:
4. Define a Simple pendulum?
5. Terms related to simple pendulum:
6. What is the unique property of Quartz?
7. Which clock is used to measure the Short Interval of time?
8. What are digital clocks?
9. What is an atomic clock?
10.Define Timer?
11. What are units of Time?
12. What is an optical Lattice clock?
Motion
1. What is rest?
2. When an object is said to be in Motion?
3. Different types of Motion
4.Falcon
5.Cheetah
6. Slow motion
7. Fast Motion
8. Define speed?
9.Define Speedometer?
10. Define Odometer?
11.Difference between Uniform and non uniform motion?
***************************************************************************
1. What are time measuring devices in ancient times?
Important time measuring devices used in ancient times are Sundial, Sand clock, Water clock.
2.What are natural events our ancestors used to measure time?
- Time taken between one Sunrise to next sunrise was called a ‘day’ or solar day.
- Time taken between one new moon to the next new moon was called as “month”.
- The time taken by the earth to complete one revolution of the sun was called as year.
- Maharaja of Jaipur, Sawai Jai Singh II, built the biggest Sundial in the world called “Samrat Yantra” in 1728.
3. Measurement of Time:
- Clocks and watches use the principle of periodic motion.
- A motion which repeats itself at regular intervals of time is called periodic Motion. Ex: Simple Pendulum.
4. Define Simple pendulum?
- A Simple pendulum consist of small metal ball (called bob) suspended by a long thread from a rigid Support, Such that bob is free to swing back & froth.
- Motion of pendulum was first studied by Galileo.
5.Terms related to simple pendulum:
Length of pendulum:
Length of string from point of suspension to the centre of the bob is called length of pendulum
Mean position of the bob:
The position of bob when it is at rest called its mean position.
Extreme position of bob:
The positions where the bob is at the maximum distance from the mean position are called extreme positions.
Oscillation of pendulum:
One complete to and fro motion of the bob about its mean position is called oscillation of the pendulum.
Amplitude of the pendulum:
Maximum displacement of the bob from its mean position on either side is called amplitude of the pendulum.
Time period of pendulum:
The time taken by bob of pendulum to complete one oscillation is called time period of pendulum
Frequency of pendulum:
The number of oscillations made by a pendulum in one second is called its frequency.
Frequency (f) = 1/ Time period (T)
6.What is the unique property of Quartz ?
- Quartz has unique property of oscillating when subjected to a small amount of electric current.
- Here, electric cell and Quartz crystal are placed in an electric circuit.
- Quartz clocks are more accurate than pendulum clocks
7. Which clock is used to measure Short Interval of time?
- For measuring short interval of time, stop watch is used
- It can measure 1/10th of second.
- It can be made to start or stop with help of push button
8.What are digital clocks?
- Digital clocks do not have hour, minute or second hands
- They display time in digits in both 12 or 24 hours
9. What is an atomic clock ?
- Famous atomic clock is NIST – FI cesium Fountain atomic clock
- Atomic dock invented by Louis Essen 1955
- Atomic clocks swarns of small satellite to communicate with each other and space exploration
- An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms
10.Define Timer?
- A timer is a special type of clock used to record sequence of event.
- It is used in microwaves, washing machines, traffic signals, a/c etc.
11.What are units of Time?
Standard unit of measuring time is second. It is written as ‘s’
Larger units of time are measured in
Minutes = min
Hours = ‘h’
Some units and their conversion
60 seconds = 1 minute
60 minutes = 1 hour
24 hours = 1 day
30 days = 1 month
12 month = 1 year
10 years = 1 decade
100 years = 1 century
1000 years = 1 millennium
12. What is optical Lattice clock?
- It was designed by Jerome Lodewyck and team at Paris observatory.
- It is most accurate clock and could to within every 18,000 million years.
- It uses laser beams.
- It is more than twice as accurate as atomic clock
- It is used in telecommunications and satellite navigation clocks and this can be used as standard world’s time.
Motion
1. What is rest?
An object is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with time or with respect to surroundings
2. When an object is said to be in Motion?
An object is said to be in motion when its position changes with time or with respect to its surroundings.
3. Different types of Motion
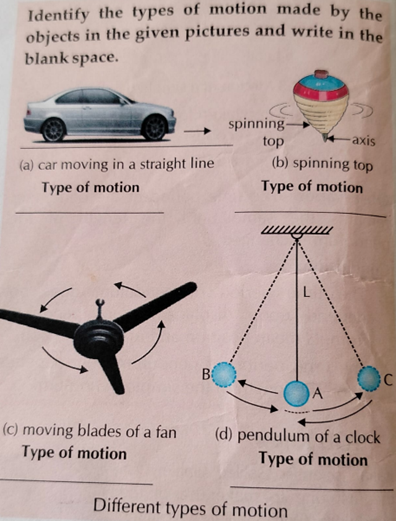
Check out class 6 Motion in detail
4.Falcon is fastest organism in the world that can fly with speed of 300km/hr.
5.Cheetah is the fastest land animal on earth that can run with speed of 112km/hr.
6. Slow motion = An object which takes longer time to cover a certain distance is said to be slow,
7. Fast Motion = An object that takes a shorter time to cover the same distance is said to be fast.
8. Define speed?
Spead of a moving object is the distance
travelled by it in a unit time.
Speed = Distance travelled / Time taken
Unit of speed = m/s for fast moving object it is Km/h
9.Define Speedometer ?
It is an instrument on a vehicle’s dashboard that indicates speed of vehicle at that instant time in km/h.
10. Define Odometer?
It is an instrument that shows the distance travelled by vehicle in km.
11.Difference between Uniform and non uniform motion?
| Uniform motion | Non uniform motion |
| 1. Uniform motion implies movement of body along a straight line with steady speed. | 1. Non uniform motion implies movement of an object along a straight line with variable speed. |
| 2. It covers equal distance in equal time interval. | 2. It covers unequal distance in equal time interval |
| 3. It is similar to actual speed of object | 3. It is different from actual speed of objects. |
| 4. Distance time graph shows straight line | 4. Distance time graph shows curved line |
| 5. There is no acceleration | 5. There is non zero acceleration |
Distance Time graph
A distance-time graph is a graphical representation of how the distance covered by an object changes with time. It helps us analyze the motion of an object easily.
How to Draw a Distance-Time Graph?
Step 1: Draw two perpendicular axes.
Step 2: Label the X-axis as Time (seconds, minutes, hours, etc.).
Step 3: Label the Y-axis as Distance (meters, kilometers, etc.).
Step 4: Plot the points based on the given data.
Step 5: Connect the points smoothly.
Different Types of Distance-Time Graphs
Object at Rest (No Motion)
- The graph appears as a horizontal line (parallel to the X-axis).
- This means that the object is not changing its position over time (it is stationary).
- Example: A parked car or a person sitting on a bench.
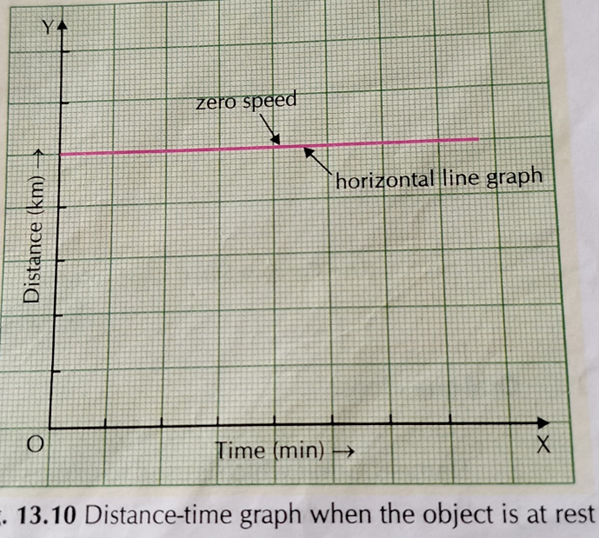
Graph Interpretation:
Time increases, but distance remains the same.
Graph Representation:
Time (seconds) | Distance (meters)
******* | *******
0 | 10
2 | 10
4 | 10
6 | 10
This will result in a straight horizontal line at distance = 10 meters.
Uniform Motion (Constant Speed)
- The graph appears as a straight slanting line.
- The object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Example: A train moving at a steady speed.
Graph Interpretation:
- As time increases, distance increases at a constant rate.
- The steeper the line, the faster the motion.
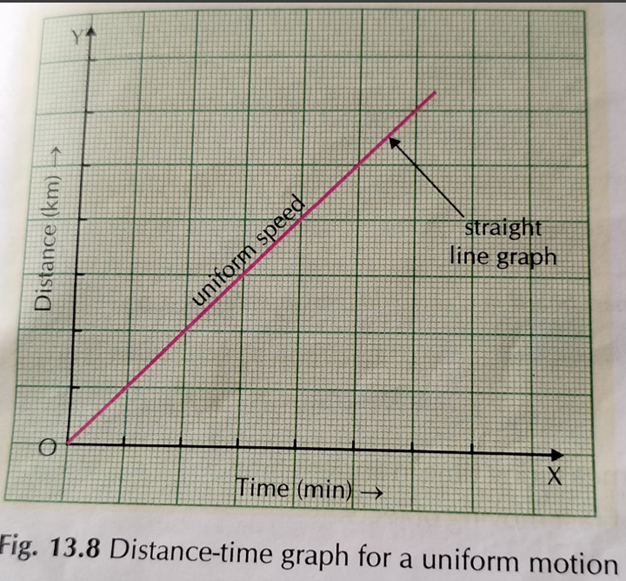
Graph Representation:
Time (seconds) | Distance (meters)
———– | ————
0 | 0
2 | 10
4 | 20
6 | 30
This will result in a straight line sloping upwards.
Non-Uniform Motion (Changing Speed)
- The graph appears as a curved line.
- The object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Example: A car moving through city traffic.
Graph Interpretation:
- The curve bends upwards if the object is accelerating (speed increasing).
- The curve bends downwards if the object is decelerating (speed decreasing).
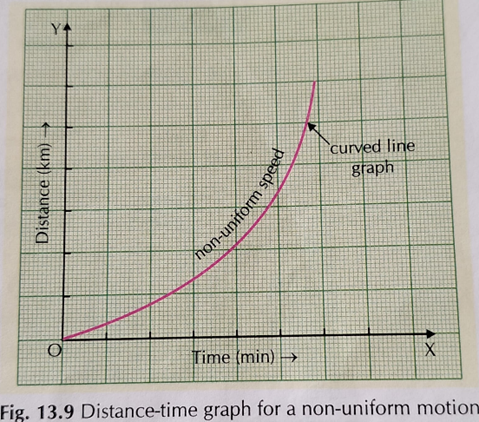
Graph Representation:
Time (seconds) | Distance (meters)
———- | ————
0 | 0
2 | 5
4 | 15
6 | 35
This will result in a curved graph, showing acceleration.
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance. It is calculated using the formula
Speed = Distance/Time
SI Unit of Speed
- The standard unit of speed is meters per second (m/s).
- Other common units include kilometers per hour (km/h) and miles per hour (mph).
Example Calculation:
- A cyclist covers 100 meters in 20 seconds.
- Speed = 100 ÷ 20 = 5 m/s.
Understanding Speed from a Graph
- A steep slope means higher speed.
- A gentle slope means lower speed.
- A horizontal line means zero speed (object at rest)
Applications of Distance-Time Graphs:
- Analyzing Vehicle Motion
- Helps in studying how fast a vehicle is moving.
- Used in speed tracking systems like GPS and speedometers.
- Predicting Travel Time
- Helps estimate the time required to reach a destination.
- Used in Google Maps and navigation apps.
- Science and Engineering
- Helps in studying the motion of planets, satellites, and space objects.
- Used in designing roads and transportation systems.
*********************************************************************************
Useful links: