Questions covered are
- Define Reproduction?
- What are the vegetative parts of a plant?
- Which part of the plant is the reproductive part?
- What are the male and female parts of a plant called?
- What are the two modes of reproduction in plants?
- What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction in plants?
- What are the methods of asexual reproduction?
- Write a short note on fragmentation.
- Write a short note on spore formation.
- Define vegetative propagation.
- Define tuber.
- What is a stem tuber?
- Write about stem bulbs.
- What is a rhizome?
- Write a short note on subaerial stems.
- Write about corms.
- How does vegetative propagation occur by roots?
- How does vegetative propagation occur by leaves?
- What are viviparous plants?
- List the artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
- Write about cutting.
- Write about layering.
- Write a short note on grafting.
- Define/explain tissue culture.
- List a few advantages of vegetative propagation.
- List a few disadvantages of vegetative propagation.
- Which part of a plant is involved in sexual reproduction?
- What are the reproductive organs of flowers?
- What is the difference between Stamen and Pistil?
- What are unisexual and bisexual flowers?
- Give examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers.
- What are the steps involved in sexual reproduction?
- Define pollination and its types.
- What is self-pollination?
- What is cross-pollination?
- What are the agents of pollination?
- How do insects help in pollination?
- How does pollination occur by wind?
- How does pollination occur by water?
- Define fertilization.
- What are the steps involved in fertilization?
- How are seeds and fruits formed after fertilization?
- What are the types of fruits? Give examples.
- Define dispersal of seeds.
- How is seed dispersal beneficial to plants?
- What are the various agents of seed dispersal?
- Give examples of seed dispersal by wind.
- Give examples of seed dispersal by water.
- Give examples of seed dispersal by animals.
- Give examples of seed dispersal by explosive mechanism.
- Define germination of seeds.
- What are the steps involved in seed germination?
***************************************************************************
Define Reproduction?
The production of new individuals from parents is known as Reproduction.
The vegetative parts of a plant are roots, stems, leaves.
Flowers are the reproductive part of a plant.
Male part of a plant is called male gamete, whereas the female part is called female gamete.
What are the two modes of reproduction in plants?
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction in plants?
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| The production of new plants from a single parent without the involvement of gametes is called asexual reproduction. | The production of new plants from existing parents by fusion of their gametes is called sexual reproduction. |
| Fusion of gametes is not involved. | Here, the gametes are involved in fusion. |
| No seeds are formed. | Seeds are formed. |
| In asexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from a single parent. | In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from existing plants through seeds. |
What are the methods of asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction takes place by fragmentation, spore formation, and vegetative propagation.
Write a short note on fragmentation.
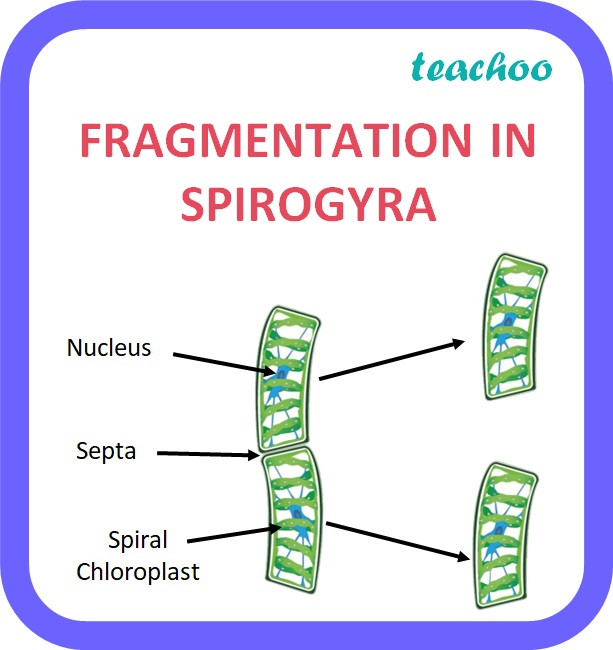
Spirogyra reproduces by the fragmentation method.
The breaking up of the body of a plant into two or more fragments where each fragment grows and matures into a new plant is called the fragmentation process.
Write a short note on spore formation.

- Spores are asexual reproductive bodies.
- Examples: Fungi, mosses.
- Spores are covered by a hard protective covering that can withstand high temperature and low humidity.
- Under favorable conditions, spores germinate into new individuals.
- Spores are produced in structures called sporangia.
Note: Fungi reproduce by another asexual method called budding.
Define vegetative propagation.
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction, in which new plants are produced from vegetative parts of the plant such as root, stem, leaves, and buds.
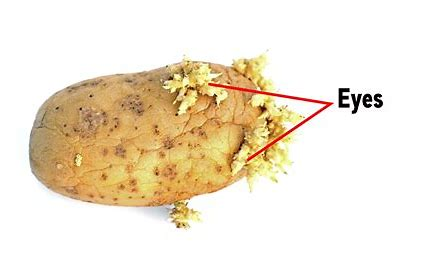
Define tuber.
A tuber is the swollen underground stem of a plant that stores food.
Stem Tuber: The underground stem of a potato is called a stem tuber. It has buds called “eyes,” from which new potato plants grow.
Write about stem bulbs?
- The underground stems of onion, tulip, and lily are called bulbs.
- These are thick, short, and have reserved food.
- These bulbs have buds that grow into new plants.
What is a rhizome?
- A rhizome is an underground stem found in plants like ginger and turmeric.
- They have scaly leaves and buds that develop into a new plant.
Write a short note on subaerial stems.
- In some plants, branches that grow from the base of the stem creep along the ground.
- These branches develop roots and new leaves when they touch the soil.
- Examples: Grasses, strawberry, mint.
Write about corms?
- Corms are thickened, round stems with stored food.
- These give rise to new plants.
Vegetative propagation by roots?
- In sweet potato, dahlia, and tamarind, root cuttings with buds can form a new plant when placed in moist soil.
Vegetative propagation by leaves?
- The leaves of certain plants produce buds on their margins.
- When these leaves detach and touch moist soil, they grow into a new plant.
Mangroves are viviparous plants.
List the artificial methods of vegetative propagation.
Some artificial methods of vegetative propagation are:
- Cutting
- Layering
- Grafting
- Tissue culture
Write about cutting.
- In this method, a stem with a bud is cut and planted in moist soil.
- After a few days, roots and leaves develop.
Layering:
- In this method, the lower branch of the plant is bent, and a small portion of it is covered with moist soil.
- The bark of the covered portion is removed before covering with soil.
- After a few days, roots develop in the buried portion of the branch.
- The branch is then cut from the main plant, and it grows as an independent plant.
- Examples: Bougainvillea, Jasmine, Rose.
Write a short note on grafting?
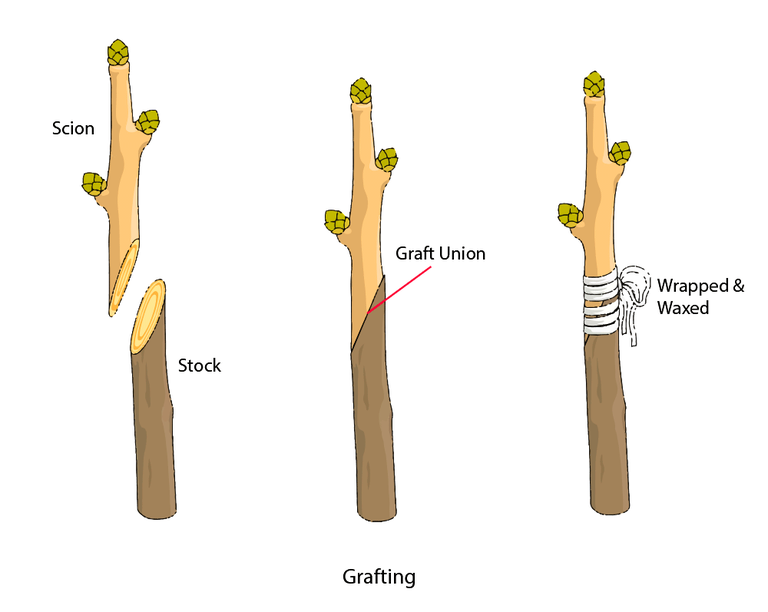
- This method is used to develop new and better varieties by combining two plants.
- The stem (Scion) of one plant is stump to another plant with a rooted stem (Stock).
- The stems of Scion and Stock are obliquely cut and placed one above another.
- These are bound tightly with cloth or polythene sheet to avoid infection and loss of water from the cut surface.
- After a few days, new cells develop, joining the Scion and Stock together.
- Examples: Mango, Rose, Pear, Lemon, etc.
Define/Explain about tissue culture?
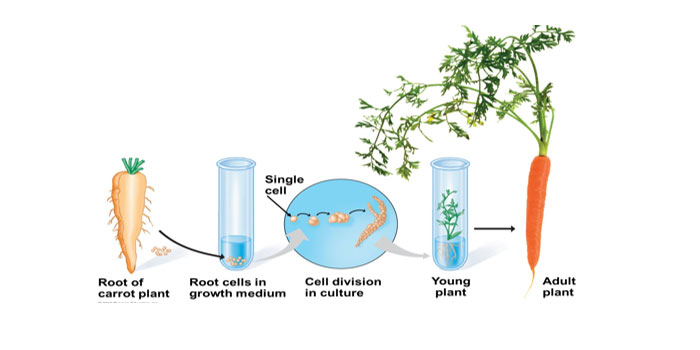
- The tiny part of plant tissue is called an explant.
- Tissue culture is a technique of growing new plants from an explant in a culture of synthetic medium under aseptic conditions.
- Cells of tissue divide and grow into an unorganized mass of cells called callus.
- Hormones are added to induce plant growth.
- Thousands of plantlets can be formed using this technique.
- These plantlets are transported into moist soil for further growth.
- Examples: Orchids, Asparagus, Chrysanthemum.
List a few advantages of vegetative propagation?
a) It is a quick method to multiply plants.
b) Plants grown by this method mature in less time and bear more fruits.
c) The new plants produced are exact copies of the parent plant.
d) Seedless plants like banana, sugarcane, pineapple are grown by this method.
e) Plants produced from vegetative propagation require less attention.
List a few disadvantages of vegetative propagation?
- Diseases in the parent plant spread to all the offspring.
- Vegetative propagules cannot be stored like seeds.
- Vegetatively propagated plants are unable to adapt to changing environments.
Flowers
- Plants with flowers have characteristics of sexual reproduction.
- The reproductive part of a plant is the flower.
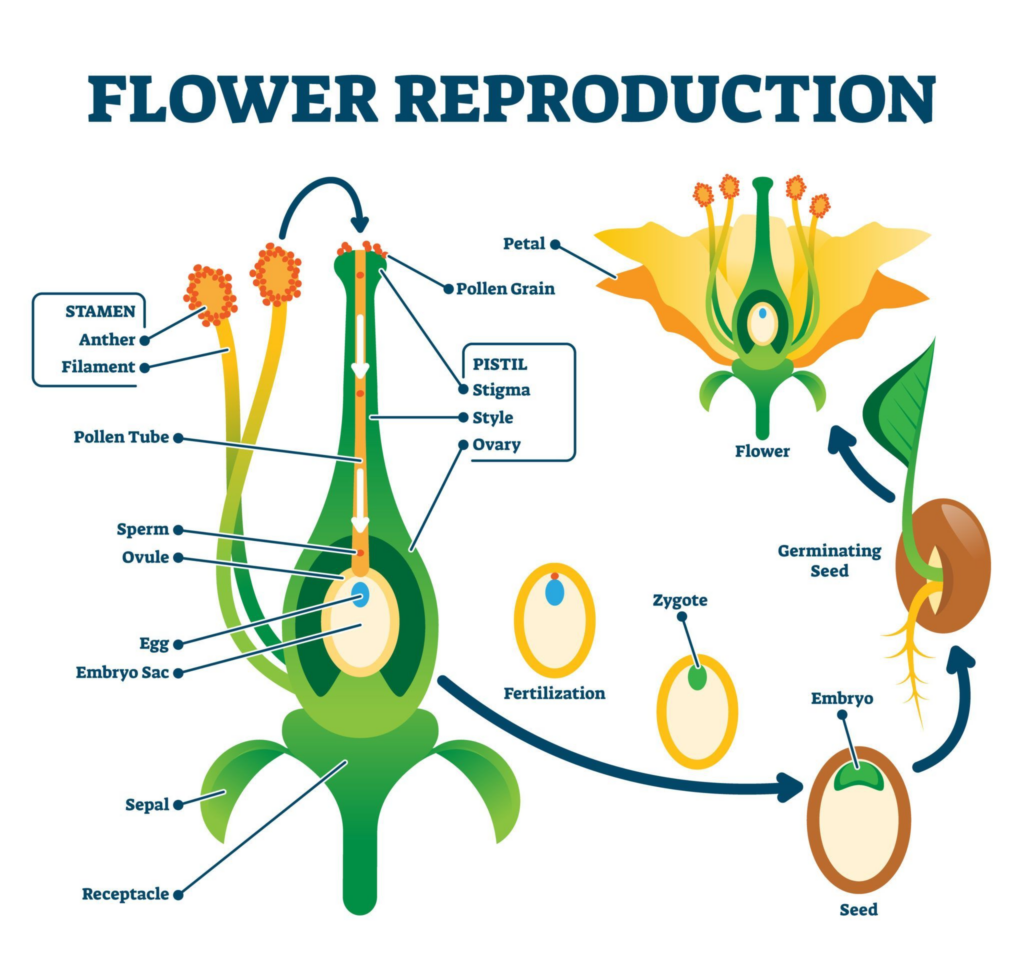
- The reproductive organs of flowers are stamen and pistil.
Write the difference between Stamen and Pistil.

| Stamen (Male Reproductive Organ) | Pistil (Female Reproductive Organ) |
| Stamen is the male reproductive organ of plants. | Pistil is the female reproductive organ of plants. |
| It has two parts: Anther and Filament. | It has three parts: Stigma, Style, and Ovary. |
| The swollen tip of the stamen is called the anther, and the stalk is called the filament. | The top sticky part of the pistil is called the stigma, the middle part is the style, and the swollen base is the ovary. |
| Anther contains pollen grains. | Ovary contains ovules. |
| Pollen grains contain male gametes. | Ovules produce female gametes. |
| Pollen grains appear as yellow, powdery substances. | Each ovule contains only one female gamete called an egg. |
Differences Between Unisexual and Bisexual Flowers
| Unisexual Flowers | Bisexual Flowers |
| The flowers which contain only one reproductive organ (either pistil or stamen) are called unisexual flowers. | The flowers which contain both reproductive organs (pistil and stamen) are called bisexual flowers. |
| Also called incomplete flowers. | Also called complete flowers. |
| Examples: Papaya, Cucumber, Pumpkin, Watermelon, etc. | Examples: Rose, Mustard, Gulmohar, Lily, etc. |
Steps Involved in Sexual Reproduction
The steps in sexual reproduction are:
- Pollination – Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma.
- Fertilization – Fusion of male and female gametes.
- Formation of Seed and Fruit – After fertilization, ovules develop into seeds and the ovary becomes the fruit.
- Germination of Seed – The seed develops into a new plant under suitable conditions.
Definition of Pollination and Its Types
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
The two types of pollination are:
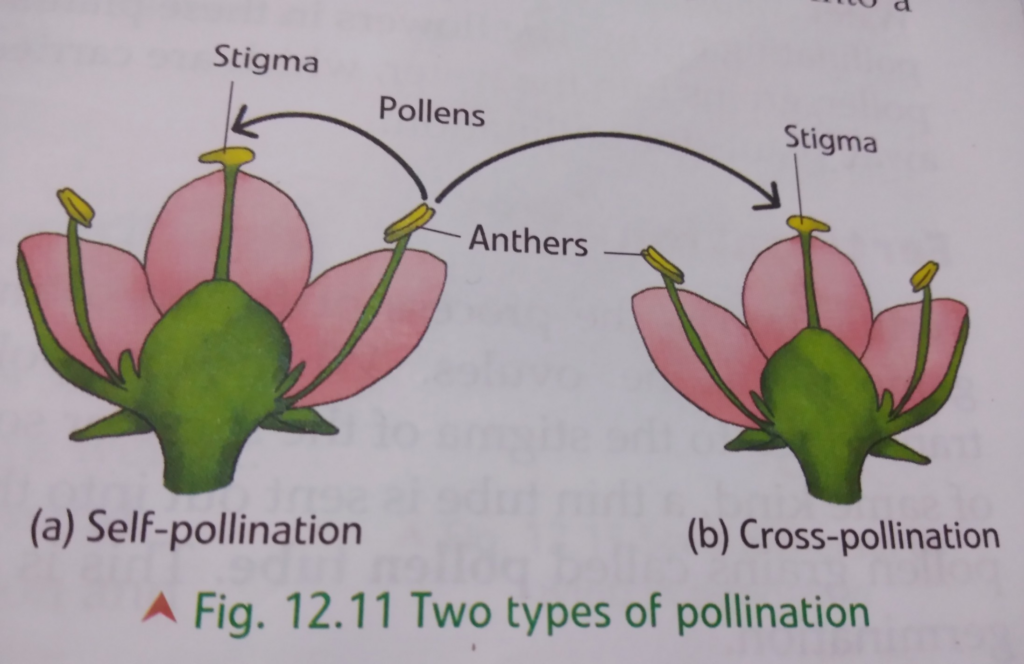
- Self-pollination
- Cross-pollination
Self-Pollination
When pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower (or another flower of the same plant), it is called self-pollination.
Cross-Pollination
When pollen grains from the anther of a flower of one plant are transferred to the stigma of a flower of another plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination.
Agents of Pollination
Pollination occurs through different agents, such as:
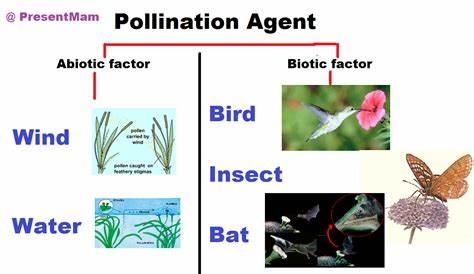
- Pollination by Insects
- Pollination by Wind
- Pollination by Water
How Do Insects Help in Pollination?
- Large, bright-colored, sweet-scented flowers attract insects.
- When insects visit a flower, pollen grains from anther stick to their bodies.
- When they sit on another flower, the pollen grains rub off on the stigma, resulting in pollination.
How Does Pollination Occur by Wind?
- When pollen grains mature, the anthers break open to release them.
- The blowing wind carries the mature pollen grains to the stigma of another flower.
- Ex: Grass, Wheat, Corn, Sugarcane, Rice, Maize etc.
Pollination by Water
- The water currents carry mature pollen grains from one flower to another and help in pollination.
- Example: Vallisneria and Hydrilla.
Define Fertilization
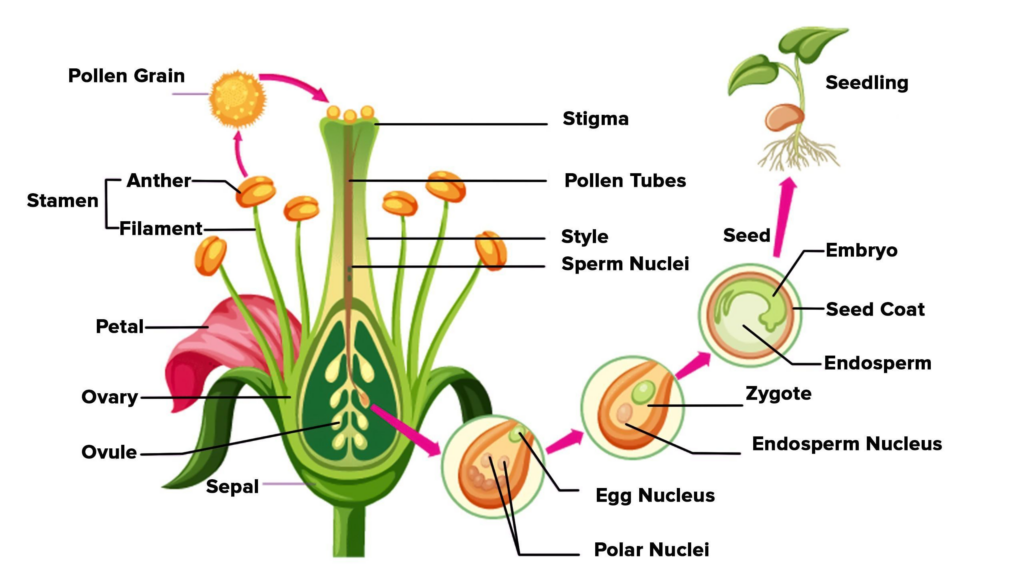
- The fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete to produce a zygote is called fertilization.
Write the Steps Involved in Fertilization
- When a pollen grain falls on the stigma, it grows as a pollen tube that moves downward.
- The pollen tube penetrates the stigma, passes through the style, and enters the ovule.
- The male gamete moves down to the ovule through the pollen tube.
- The tip of the pollen tube bursts open, and the male gamete comes out of the pollen tube.
- The male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote.
How Are Seeds and Fruits Formed After Fertilization?
- The ovary of the flower swells and develops into a fruit.
- Ovules in the ovary grow and become seeds.
- The seed contains an embryo (baby plant) and has one or two cotyledons, which store food.
- The seed is protected by a seed coat.
- Other flower parts (stamens, style, stigma) dry up and fall off.
- Types of Fruits:
- Soft, fleshy fruits – Example: Mango, Orange
- Hard, woody fruits – Example: Almond, Walnut
Define Dispersal of Seeds
- The scattering of seeds over a large area away from the mother plant by agents of dispersal is called dispersal of seeds.
How is Seed Dispersal Beneficial to Plants?
- It helps to prevent overcrowding of plants in a particular area.
- It helps the growing plant to grow in new places/new areas.
- It prevents competition for water, minerals, and sunlight among the same kind of plants.
Various Agents of Seed Dispersal
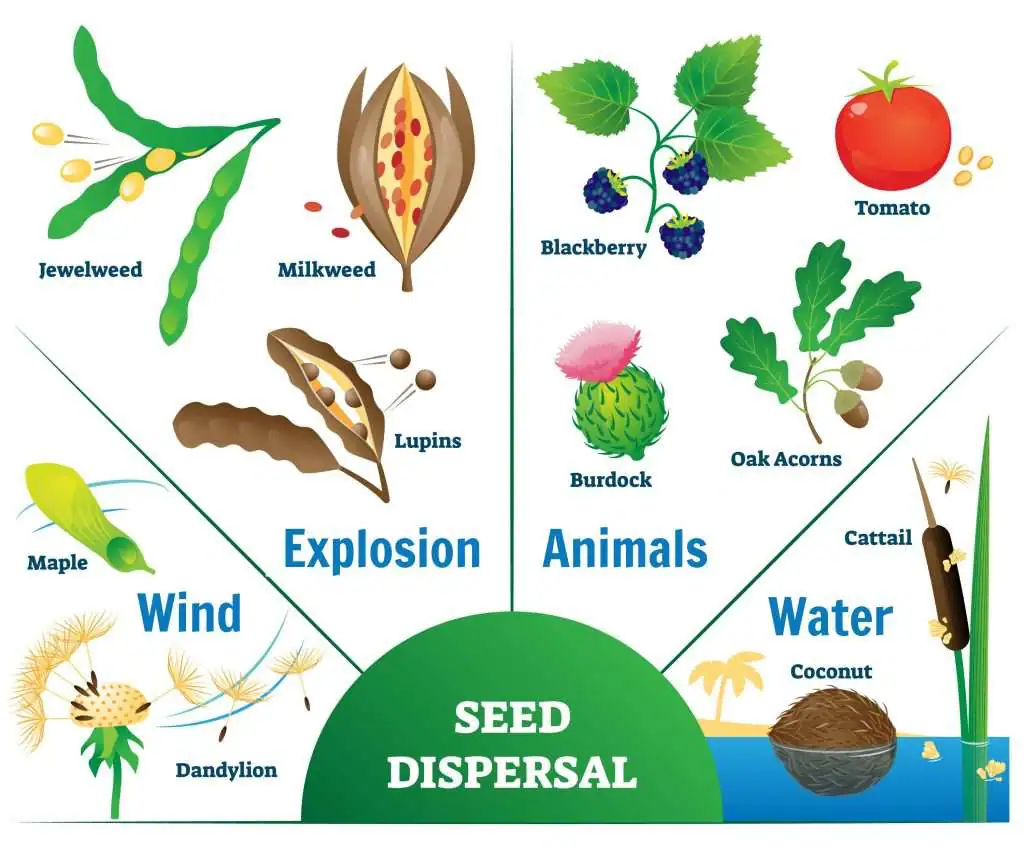
1. Dispersal by Wind
- Example: Drumstick plant, Maple plant, Dandelion, Orchids, Begonia
2. Dispersal by Water
- Example: Coconut fruits, Water lily, Lotus plant
3. Dispersal by Animals
- Example: Gokhru, Xanthium, Urena
4. Dispersal by Explosive Mechanism
- Example: Castor, Pea, Geranium
Define Germination of Seeds
- The process in which a seed begins to grow into a baby plant under favorable conditions is called germination of seeds.
Steps Involved in Seed Germination
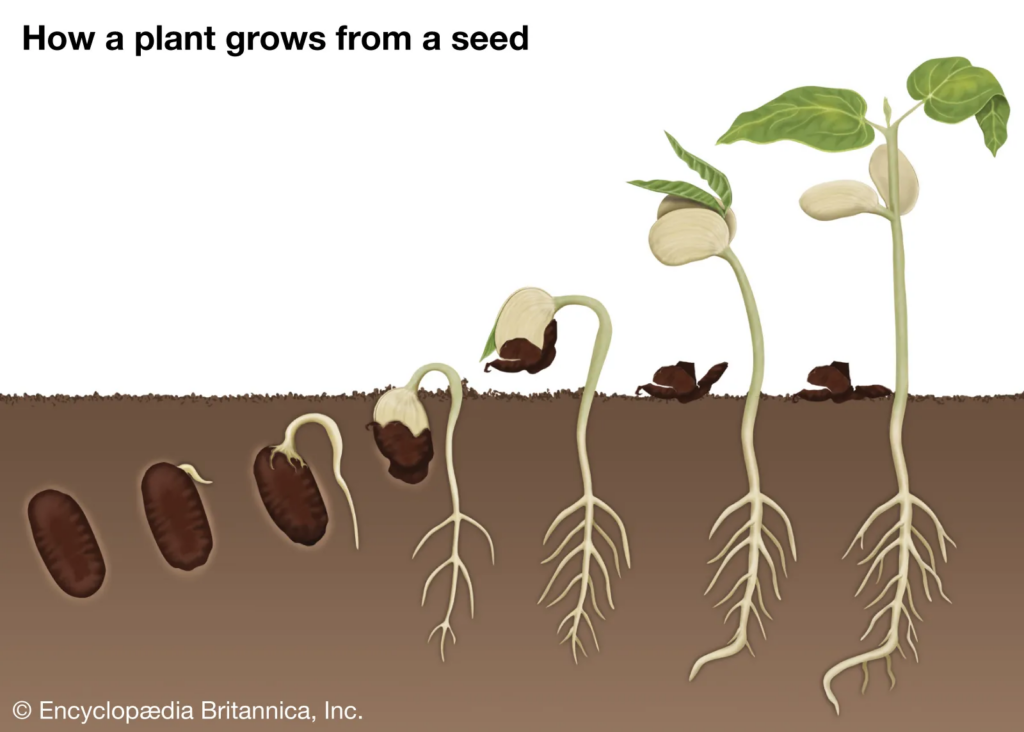
- When a seed is sown in moist soil, it soaks up water and swells.
- The seed coat splits open, and the radicle grows first to form the root system.
- The plumule moves upward and forms a new shoot.
- Green leaves develop in the shoot. They use sunlight, water, and oxygen (O₂) to carry out the photosynthesis process and prepare their own food.
- This grows into a new plant, and the cycle continues.
Useful links:
