class 7 physical and chemical change notes
Class 7 Physical and Chemical change (Phy)
Questions covered are:
Q1: What is a physical change? Provide detailed examples.
Q2: What is a chemical change? Provide detailed examples.
Q3: How can we distinguish between physical and chemical changes?
Q4: Why is rusting of iron considered a chemical change?
Q5: What are the conditions necessary for rusting?
Q6: How can rusting of iron be prevented?
Q7:Difference between Crystallization and Evaporation
Q8: Explain the reaction of vinegar and baking soda?
Q9. Why is burning a candle both a physical and chemical change?
Book back questions with answers:
***********************************************************************
Q1: What is a physical change? Provide detailed examples.
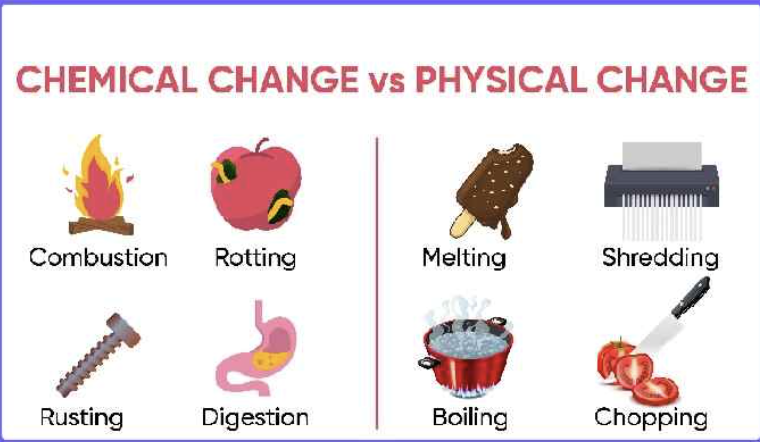
A physical change involves alterations in the physical properties of a substance—such as shape, size, color, or state—without changing its chemical composition.
Characteristics:
- No new substance is formed.
- Generally reversible; the original substance can be recovered.
- Only physical properties change; chemical properties remain unchanged.
Detailed Examples:
Melting of Ice:
- Solid ice absorbs heat and changes into liquid water.
- The molecular structure remains H₂O; only the state changes from solid to liquid.
- By freezing, water can revert to ice.
Dissolving Sugar in Water:
- Process: Sugar crystals disperse in water, forming a homogeneous solution.
- Explanation: Sugar molecules remain unchanged chemically; they’re just dispersed within the water.
- Reversibility: Evaporating the water will recrystallize the sugar.
Tearing of Paper:
- Process: Paper is torn into smaller pieces.
- Explanation: The chemical composition of the paper fibers remains unchanged; only the size and shape are altered.
- Reversibility: Physically rejoining the pieces is challenging, but no new substances are formed.
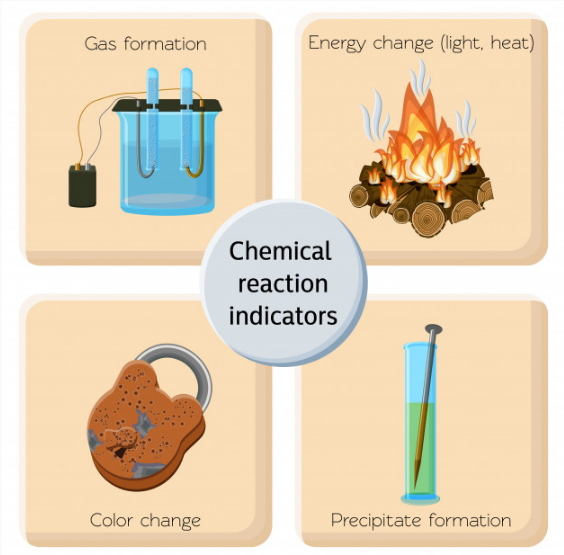
Q2: What is a chemical change? Provide detailed examples.
A chemical change, or chemical reaction, results in the formation of one or more new substances with properties different from the original substances.
Characteristics:
- New substances with distinct properties are formed.
- Usually irreversible by simple physical means.
- Both physical and chemical properties of the original substances change.
Examples:
Rusting of Iron:
- Process: Iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture, forming iron oxide (rust).
- Chemical Equation: 4Fe + 3O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃
- Explanation: The iron surface undergoes oxidation, producing a brownish-red flaky substance different from metallic iron.
- Irreversibility: Returning rusted iron to pure iron requires industrial processes.
Burning of Wood:
- Process: Wood combusts in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide, water vapour, ash, and heat.
- Explanation: Complex organic compounds in wood break down, forming new substances like gases and ash.
- Irreversibility: Ash and gases cannot be recombined to form the original wood.
Digestion of Food:
- Process: Enzymes break down food molecules into simpler substances the body can absorb.
- Explanation: Complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are chemically transformed into simpler sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids.
- Irreversibility: The original food cannot be reconstituted from the digested products.
Q3: How can we distinguish between physical and chemical change?
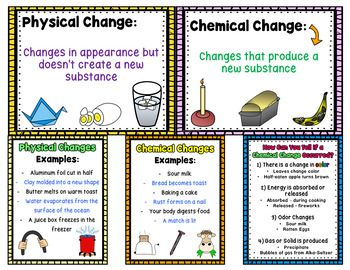
| Aspect | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| Formation of New Substance | No new substance is formed. | One or more new substances are formed. |
| Reversibility | Generally reversible by physical means. | Usually irreversible by simple physical means. |
| Energy Change | It may involve small energy changes (e.g., absorption or release of heat). | Often involves significant energy changes (e.g., heat, light, sound). |
| Examples | Melting ice, dissolving sugar in water, tearing paper. | Rusting of iron, burning wood, digestion of food. |
Q4: Why is rusting of iron considered a chemical change?
- Formation of a New Substance:
- Rusting produces iron oxide, which has different properties from elemental iron.
- Irreversibility:
- Once iron has rusted, returning it to its original state requires complex processes like electrolysis.
- Property Changes:
- Rust (iron oxide) is brittle and crumbly, lacking the strength and malleability of pure iron.
Q5: What are the conditions necessary for rusting?
- Presence of Moisture:
- Water acts as a medium, facilitating the electrochemical reactions between iron and oxygen.
- Presence of Oxygen:
- Oxygen reacts with iron atoms, leading to the formation of iron oxide (rust).
- Accelerating Factors:
- Electrolytes: Salts or acids in water can speed up rusting by enhancing electrical conductivity.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of rusting.
Q6: How can rusting of iron be prevented?
- Preventive Methods:
| Method | Description |
| Painting or Coating | Applying paint, oil, or grease creates a barrier, preventing moisture and oxygen from contacting the iron surface. |
| Galvanization | Coating iron with a layer of zinc protects it, as zinc is more reactive and corrodes preferentially, safeguarding the iron beneath. |
| Alloying | Mixing iron with other metals (e.g., chromium, nickel) to form stainless steel, |
Q7:Difference between Crystallization and Evaporation
| Feature | Crystallization | Evaporation |
| Definition | Process of forming pure crystals from a solution. | Process of removing water from a solution by heating. |
| Purity of Product | Produces pure crystals. | Produces impure solid. |
| Example | Formation of copper sulfate crystals from a solution. | Obtaining salt by evaporating seawater. |
Q8: Explain the reaction of vinegar and baking soda?
- When vinegar (acetic acid) is mixed with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate), carbon dioxide gas is released.
- Reaction:
Acetic acid (Vinegar) + Sodium bicarbonate → Carbon dioxide + Water + Other substances - Observation: Bubbles are formed due to CO₂ gas, showing a chemical change.
Q9. Why is burning a candle both a physical and chemical change?
- Physical Change: Wax melts when heated (solid to liquid).
- Chemical Change: Wax burns to produce new substances (carbon dioxide and water vapor).
- Other Examples are cooking food, the ripening of fruits.
******************************************************************
Book back questions with answers:
1. Classify the changes involved in the following processes as physical or chemical changes:
| Process | Type of Change | Explanation |
| (a) Photosynthesis | Chemical Change | A new substance (glucose) is formed, and it is irreversible. |
| (b) Dissolving sugar in water | Physical Change | No new substance is formed; sugar can be recovered by evaporation. |
| (c) Burning of coal | Chemical Change | Carbon in coal reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and ash. |
| (d) Melting of wax | Physical Change | Wax changes from solid to liquid without forming a new substance. |
| (e) Beating aluminum to make foil | Physical Change | Only the shape of aluminum changes; no new substance is formed. |
| (f) Digestion of food | Chemical Change | Food is broken down into simpler substances with different properties. |
2. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, provide the correct statement.
| Statement | True/False | Corrected Statement (if false) |
| (a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change. | False | Cutting wood is a physical change as no new substance is formed. |
| (b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change. | False | Formation of manure is a chemical change because decomposition occurs. |
| (c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily. | True | Zinc prevents iron from coming into contact with air and moisture. |
| (d) Iron and rust are the same substances. | False | Rust is iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), which is different from iron (Fe). |
| (e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change. | True | Condensation is a physical change as water vapor changes back into liquid water. |
3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
(b) The chemical name of baking soda is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃).
(c) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are galvanization and painting.
(d) Changes in which only physical properties of a substance change are called physical changes.
(e) Changes in which new substances are formed are called chemical changes.
4. When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed with the evolution of a gas. What type of change is it? Explain.
- When baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO₃) is mixed with lemon juice (citric acid), a chemical reaction occurs, producing carbon dioxide gas.
- The formation of a new substance (carbon dioxide gas) and bubbles indicates a chemical change.
Reaction:
Citric acid+Sodium bicarbonate→Carbon dioxide (CO₂)+Water+Other substances
5. When a candle burns, both physical and chemical changes take place. Identify these changes. Give another example where both changes occur.
- Physical Change: Wax melts (solid to liquid), which can solidify back.
- Chemical Change: Wax burns, producing carbon dioxide, water vapor, and soot, which are new substances.
Another example:
- Cooking of food:
- Physical Change: Water evaporates, vegetables soften.
- Chemical Change: Food gets cooked, forming new substances with different tastes and smells.
6. How would you show that setting of curd is a chemical change?
- When milk turns into curd, a new substance with different properties and taste is formed.
- The change is irreversible as milk cannot be obtained back.
- This happens due to the action of lactic acid bacteria, which break down lactose into lactic acid.
7. Explain why burning of wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered different types of changes.
- Cutting wood:
- Physical Change – The shape and size change, but the wood remains the same substance.
- Burning wood:
- Chemical Change – Wood burns to produce ash, carbon dioxide, and smoke, forming new substances.
8. Describe how crystals of copper sulfate are prepared.
Steps to prepare copper sulfate crystals:
- Dissolve some copper sulfate in a cup of hot water to make a saturated solution.
- Filter the solution to remove impurities.
- Allow the solution to cool without disturbing it.
- Crystals start forming after some time.
- Collect and dry the crystals.
Observation: Large, blue copper sulfate crystals appear, showing a physical change.
9. Explain how painting an iron gate prevents rusting.
- Rusting occurs when iron reacts with oxygen and water to form iron oxide.
- Painting forms a protective layer that prevents iron from coming into contact with air and moisture.
- This prevents the rusting process.
10. Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
- Rusting requires oxygen and moisture (water vapor).
- Coastal areas have high humidity, which speeds up rusting.
- Deserts have low humidity, slowing down rusting.
11. The gas we use in the kitchen is called liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). In the cylinder, it exists as a liquid. When it comes out from the cylinder, it becomes a gas (Change – A), then it burns (Change – B). Which of the following statements is correct?
Answer: (ii) Process – B is a chemical change.
- Process A (LPG changing from liquid to gas): Physical change (Only state changes).
- Process B (Burning of LPG): Chemical change (New substances like CO₂, water vapor, and heat are produced).
12. Anaerobic bacteria digest animal waste and produce biogas (Change – A). The biogas is then burnt as fuel (Change – B). Choose the correct statement.
Answer: (iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
- Process A (Biogas formation): Chemical change (Organic matter is broken down into methane gas).
- Process B (Burning of biogas): Chemical change (Methane burns to form carbon dioxide and water).