class 7 light notes
Class 7 Light (Physics)
Questions covered are :
1.How does light enable us to see the objects around us?
2. What is the Reflection of light?
3. Describe the terms in the Reflection of light by a plane mirror?
4. What is the difference between real and virtual images?
5. What are the characteristics of an image formed by a plane mirror?
6. What are spherical mirrors?
7. Difference between concave and convex mirrors?
8. Explain Some terms related to Spherical mirror?
9. Distinguish plane mirror, concave mirror, convex mirror?
10. How the images are formed by concave mirrors?
11. How the images are formed in the Convex mirror?
12. Define lens?
13. Difference between a Convex lens and a Concave lens?
14. Explain the terms related to spherical lens
15. How images are formed by a Convex lens?
16. How images are formed by the Concave lens?
17. Define Dispersion of light?
18. Define spectrum of white light ?
********************************************************
1.How does light enable us to see the objects around us?
- Light is a form of energy
- When sunlight falls on any object, object reflects the sunlight falling on it in all directions
- When sunlight reflected by object enters our eyes, we see the objects.
- Thus, light enable us to see the object from which it comes after reflection.
- Light travels in straight line.
2. What is the Reflection of light?
The process of sending back the light rays which fall on the surface of the object is called Reflection of light
3. Describe the terms in the Reflection of light by a plane mirror?
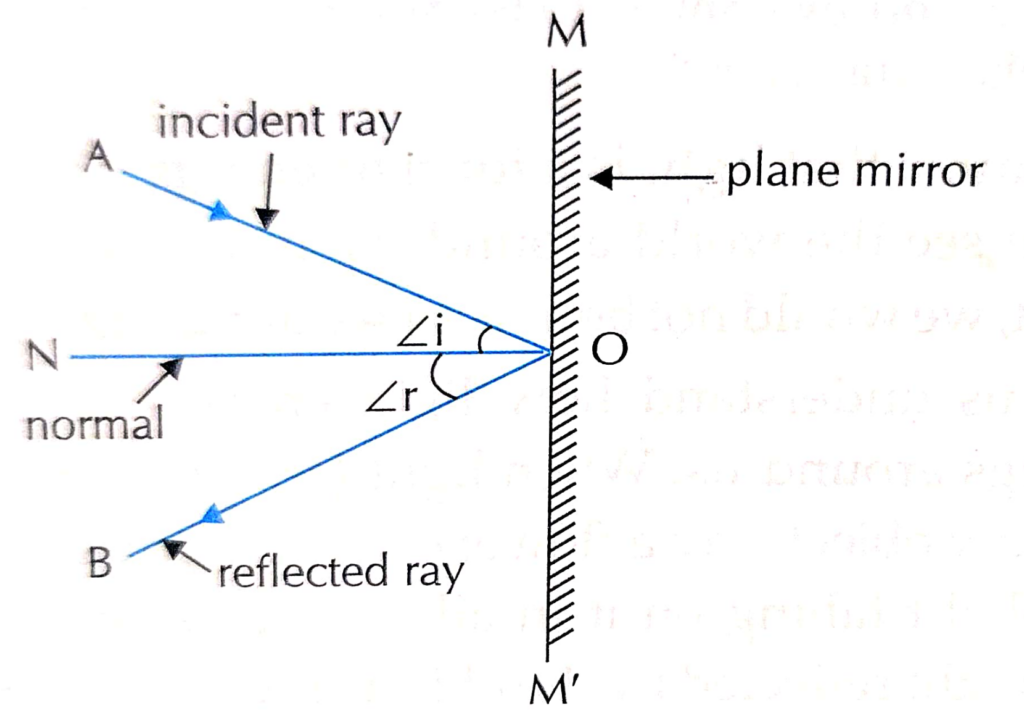
- Ray of light that falls on polished smooth surface of an object is called incident ray
- Ray of light which is sent back by surface of object is called Reflected ray
- Angle between the incident ray and normal is called angle of incidence.
- Angle between reflected ray and normal is calledangle of reflection
- Incident ray and reflected ray make equal angles with normal to a plane mirror
4. Difference between real and virtual image?
| Real image | Virtual image |
| 1. The image that can be obtained on a screen is called a real image. | 1.The image which cannot be obtained on a screen is called a Virtual image |
| 2. The real image is always inverted. | 2. Virtual image is always erect (upright) |
| 3. The image is formed on the same side of the mirror where the object is placed. | 3. Image is always formed behind the mirror |
| 4. Images of actors on screen in cinema hall are real images. | 4. Our image is in a plane mirror is an example of virtual image |
5. What does plane mirror form the characteristics of the image?
The image formed on plane mirror is
- of the Same size and shape of the object
- virtual and erect
- laterally inverted with respect to the object
- at the same distance from the mirror as the object.
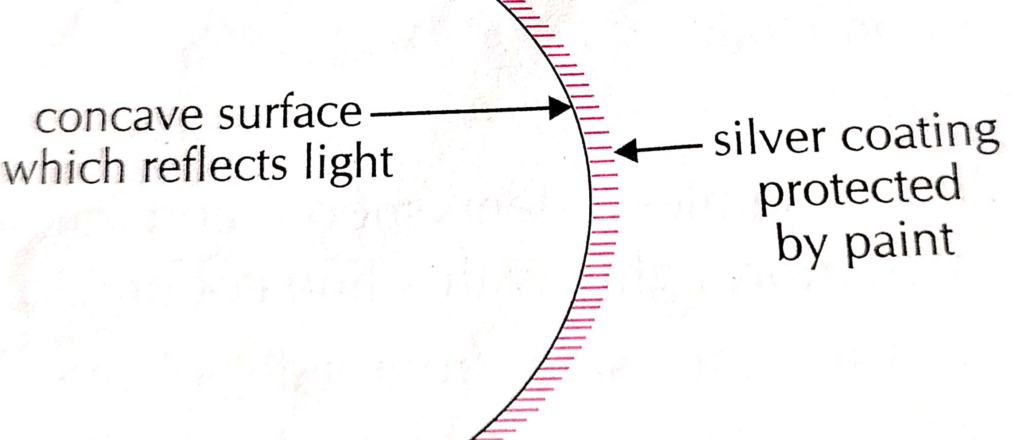
6. What are spherical mirrors?
A spherical mirror that mirror whose smooth and polished reflecting surface is a curved surface.There are 2 types of spherical mirrors
a) Concave mirror
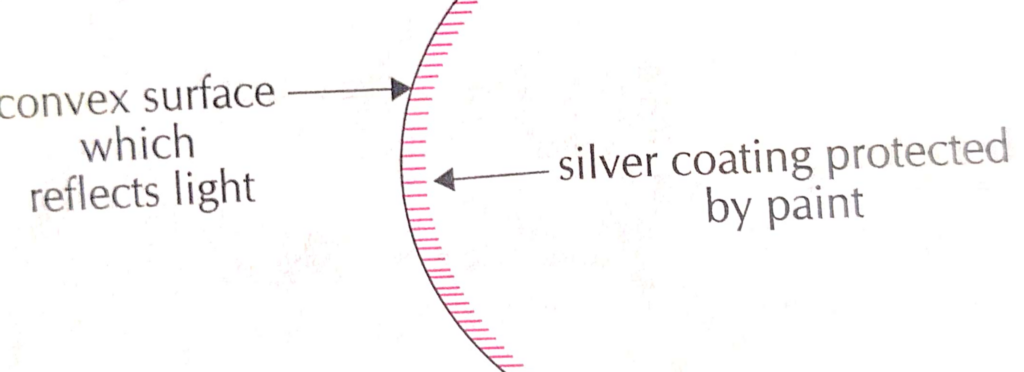
b) Convex mirror.
7. Difference between concave and convex mirrors?
| Concave mirror | Convex mirror |
| 1. A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards is called a concave mirror | 1. A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards is called a convex mirror |
| 2. Here, a reflection of light takes place at the concave surface of the mirror | 2. Here, reflection of light takes place at convex surface of mirror |
| 3. The position , nature, and size of an image formed by a concave mirror depends on the position of the object placed in front of a concave mirror | 3. For any position of the object, a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image |
| 4. Concave mirrors are used as shaving mirror, make-up mirror, reflectors in torches, and used by dentists to see enlarged image of tooth | 4. Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in car, and scooters, used as vigilance mirror in big shop, and staircase mirrors on double decker bus. |
| 5. The principal focus of the concave mirror is real and lies in front of it. | 5. The principal focus of a convex mirror is virtual and lies behind it |
8. Explain Some terms related to Spherical mirror?
Centre of curvature:
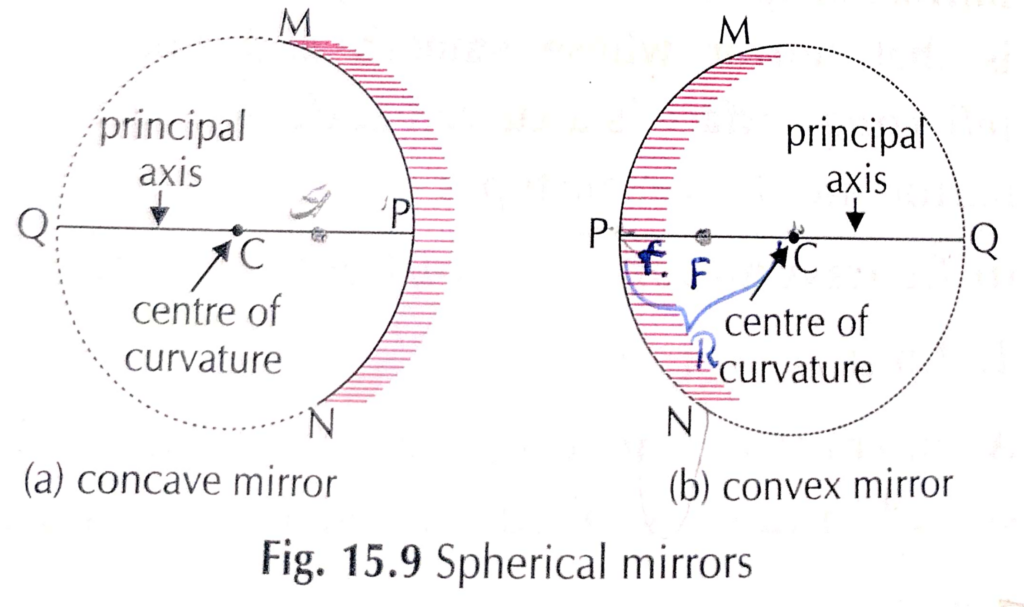
Centre of sphere of which the spherical mirror is a part is called centre of curvature of spherical mirror. “C – Centre of curvature.
Pole P :
Centre of reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called pole. `P- Pole
Pricipal axis
Imaginary line passing through centre of curvature and pole of spherical mirror is called Principal axis of mirror (PQ)
Principal focus
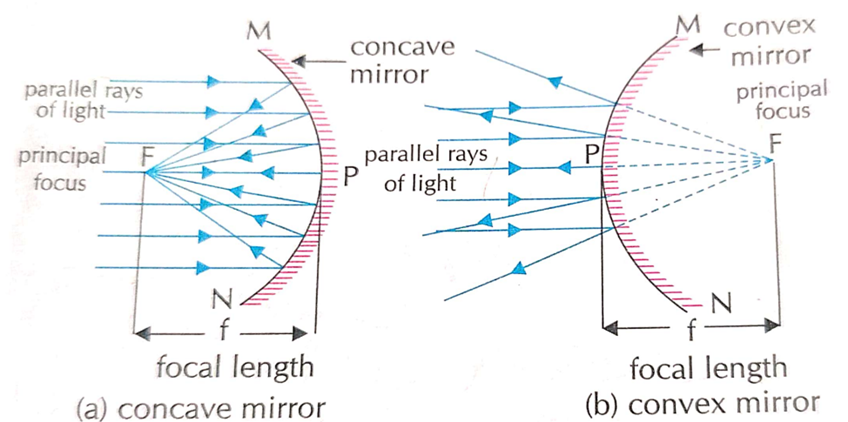
Principal focus of a spherical mirror is the point on the principal axis at which Parallel rays of light of after.
Focal length (F)
Distance between pole and focus of a spherical minor is called its focal length.
9. Distinguish plane mirror, concave mirror, convex mirror?
Plane mirror – When image is erect of same size as that of an object size and it does not change its size and nature on moving the mirror closer / away from face, mirror is plane.
Concave mirror – When image is erect, magnified and it becomes inverted on moving the mirror away from face, mirror is concave mirror
Convex mirror – When image is erect, diminished and it remains erect on moving the mirror away from face, mirror is convex mirror
10. How the images are formed by concave mirror?
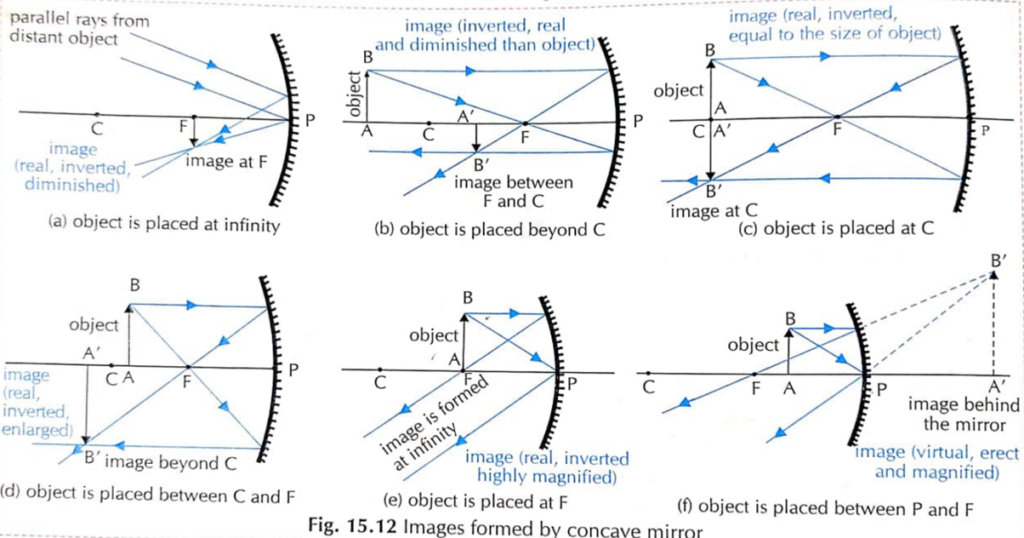
| Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of the image | Size of the image |
| At Infinity | At focus | Real and Inverted | Highly diminished |
| Beyond C | Between F and C | Real and Inverted | Smaller than the object |
| At C | At C | Real and Inverted | Equal to the size of the object |
| Between F and C | Beyond C | Real and Inverted | Larger than the object |
| At F | At infinity | Real and Inverted | Highly Magnified |
| Between P and F | Behind the mirror | Virtual and erect | Magnified |
11. How the images are formed in the Convex mirror?
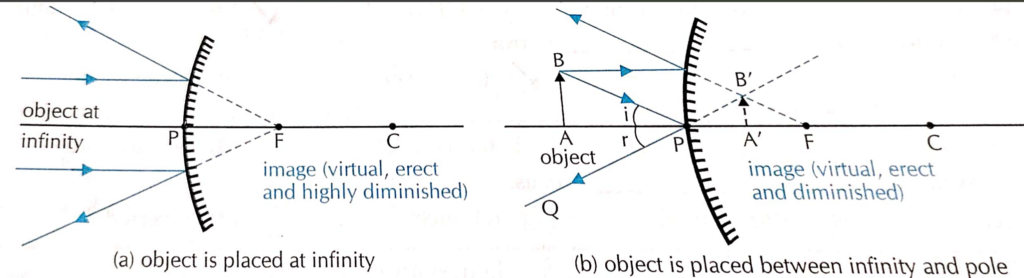
| Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of the image | Size of the image |
| At infinity | At F | Virtual and erect | Highly diminished |
| Anywhere between infinity and P | Between P and F, behind the mirror | Virtual and erect | Diminished |
12. Define lens?
- Lens is a piece of any transparent material bound by two curved surface or by one curved and one plane surface.
- When beam of light passes through lens it bends and changes its direction.
- It works on principal of refraction of light passing through them.
13. Difference between Convex lens and Concave lens?
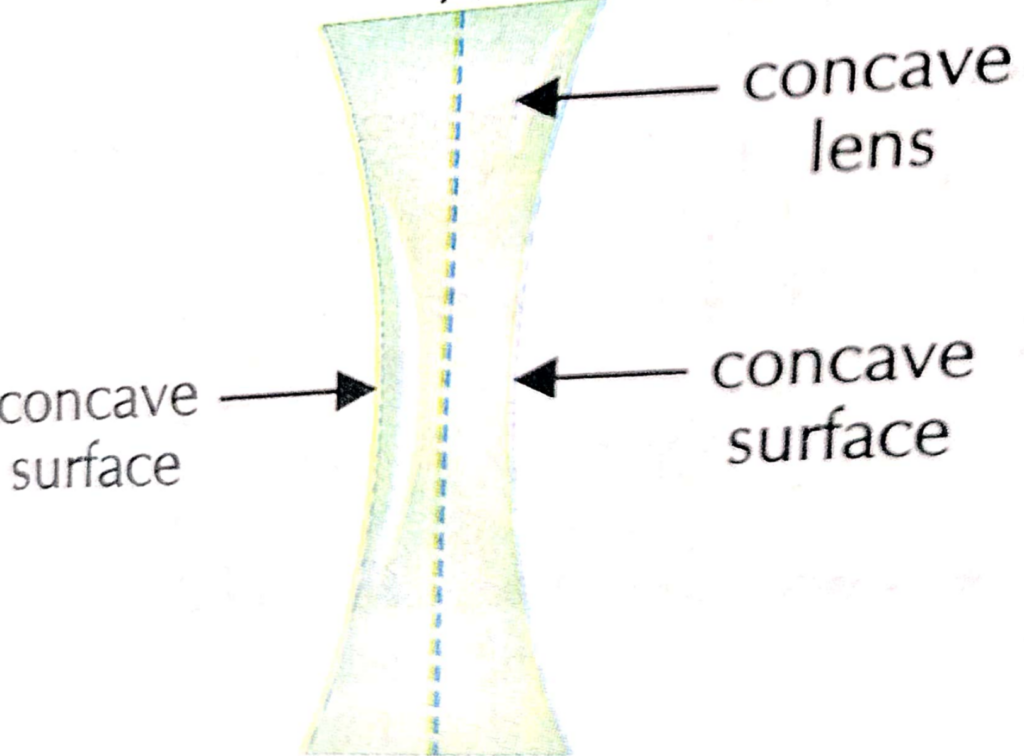
| Convex lens | Concave lens |
| 1. It is also called as converging lens | 1. It is also called as Diverging lens |
| 2. Lens which is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges is called convex lens | 2. A lens which is thinner in middle and rhicker at the edges is called as concave lens |
| 3. The image formed may be real/ virtual, enlarged/Small / equal to size of the object | 3. The image formed is always virtual and erect and smaller than the size of the object |
| 4. Convex lens are used to make magnifying glasses, spectacles, camera, microscope, telescope etc. | 4. Concave lens are used in making spectacles for people who cannot see distant objects clearly. It is used in Galilean telescope |
14. Explain the terms related to spherical lens
Principal axis
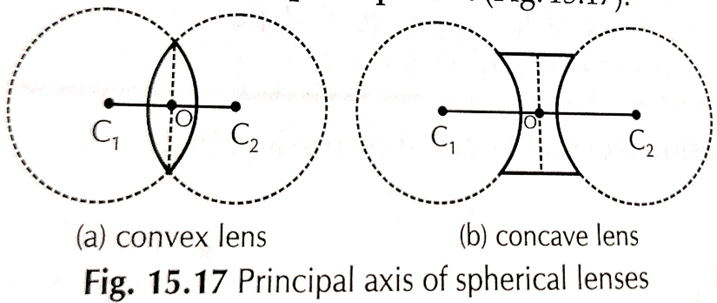
The line joining the centres of two spheres C1 and C2 of which lens form a part is called Principal axis. C1 C2 is principal axis
Optical centre
Centre of lens is called optical centre (O)
Principal focus
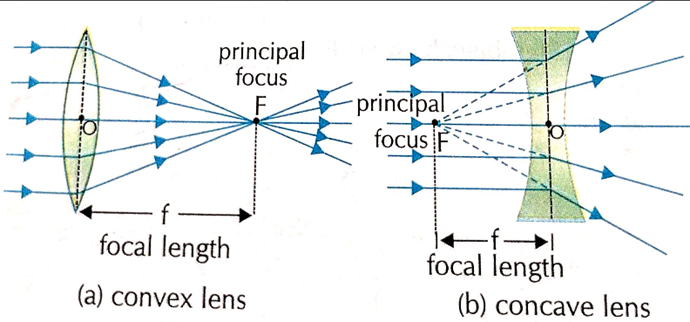
Principal focus of a spherical lens is the point on the principal axis at which parallel rays of light after passing through a lens meet / appear to meet
Focal length
Distance between the optical centre and focus of the lens is called Focal length
15. How images are formed by Convex lens ?
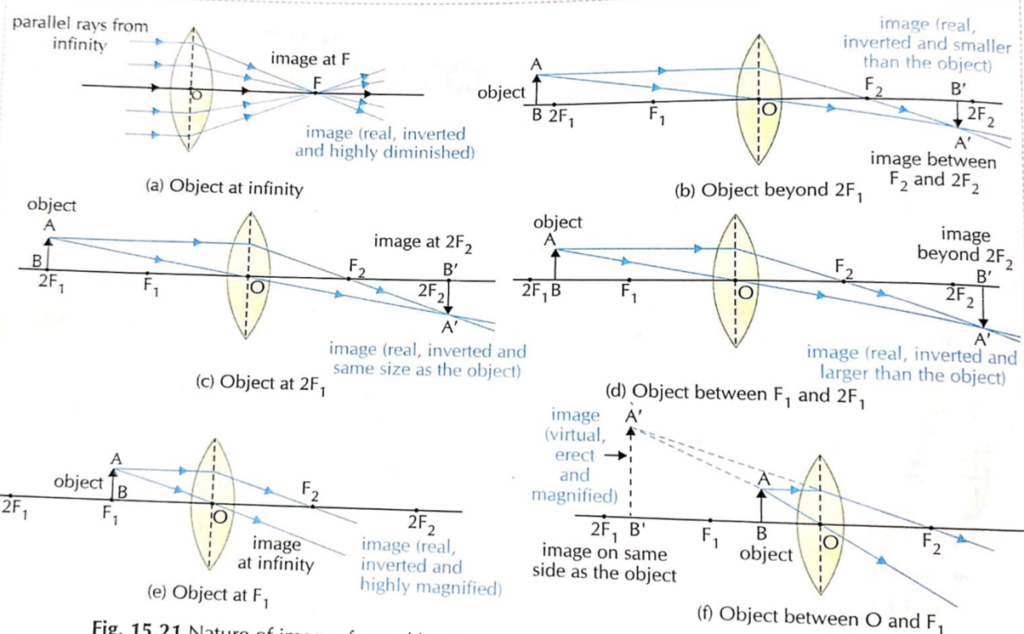
| Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of the image | Size of the image |
| At Infinity | At Focus | Real and Inverted | Highly diminished and point sized |
| Beyond 2F1 | Between F2 and 2F2 | Real and Inverted | Smaller than the object |
| At 2F1 | At 2F2 | Real and Inverted | Same size of the object |
| Between F1 and 2F1 | Beyond 2F2 | Real and Inverted | Larger than the object |
| At F1 | At Infinity | Real and Inverted | Highly magnified |
| Between O and F1 | Same side of the object | Virtual and erect | Magnified |
16. How images are formed by the Concave lens ?
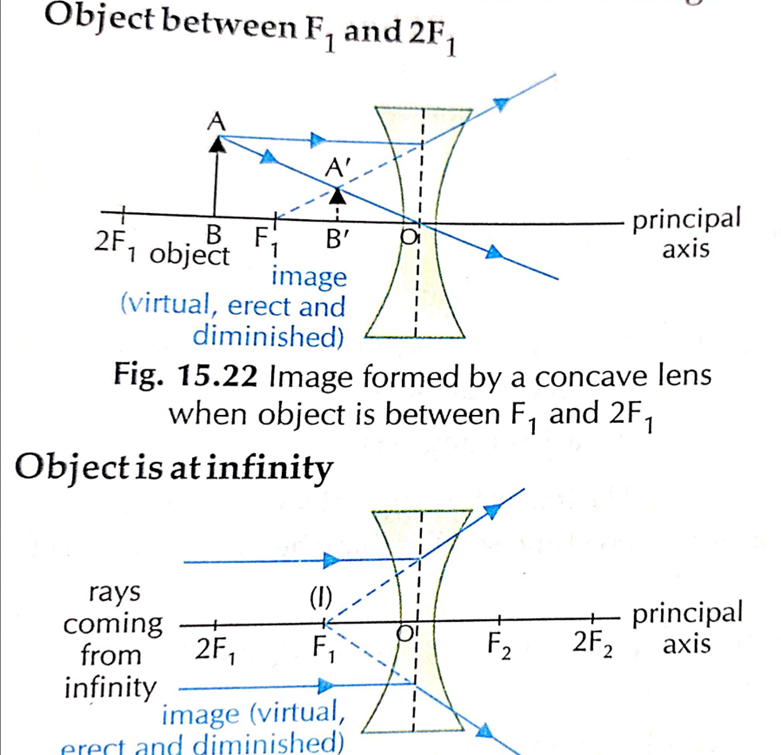
For any position of the object, a concave lens always forms a virtual , erect and diminished image
17. Define Dispersion of light?
The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its component colours on passing through prism, it is called Dispersion of light.
18. Define spectrum of white light ?
The band of seven colours formed on a white screen, when white light passes through prism is called spectrum of white light.
Sir Issac Newton was first scientist proved that white light is made up of seven colours
Useful links: