class 7 forest our lifeline notes
Class 7 – Forest Our lifeline
Forests play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life on Earth. This comprehensive Q&A guide will help students understand the importance of forests, their structure, benefits, and conservation methods.
Questions included are:
1. What is a forest?
2. What are the different types of forests?
3. What are the main components of a forest ecosystem?
4.What are the main layers of a forest?
5. Why are forests called the ‘lungs of the Earth’?
6. What are the major benefits of forests?
7.What are the causes of deforestation?
8.What are the consequences of deforestation?
9. What are the different methods of forest conservation?
10. How do forests help in preventing soil erosion?
11. How can individuals contribute to forest conservation?
12. What is the role of forests in the water cycle?
13. How do forests support biodiversity?
14. What is sustainable forestry?
15. What are some famous forests around the world?
Conclusion
********************************************************
1.What is a forest?
A forest is a large area covered with trees, plants, animals, and microorganisms that form a complex ecosystem. Forests are essential for maintaining environmental balance and provide various resources necessary for life.
2. What are the different types of forests?
Forests are classified based on climatic conditions into:
- Tropical Rainforests: Found near the equator, these forests receive heavy rainfall and have dense vegetation. Example: Amazon Rainforest.
- Temperate Forests: Found in moderate climate zones, they have distinct seasonal variations. Example: Deciduous forests in Europe.
- Boreal Forests (Taiga): Found in cold regions, mainly consisting of coniferous trees like pine and spruce. Example: Siberian Taiga.
3. What are the main components of a forest ecosystem?
A forest ecosystem consists of:
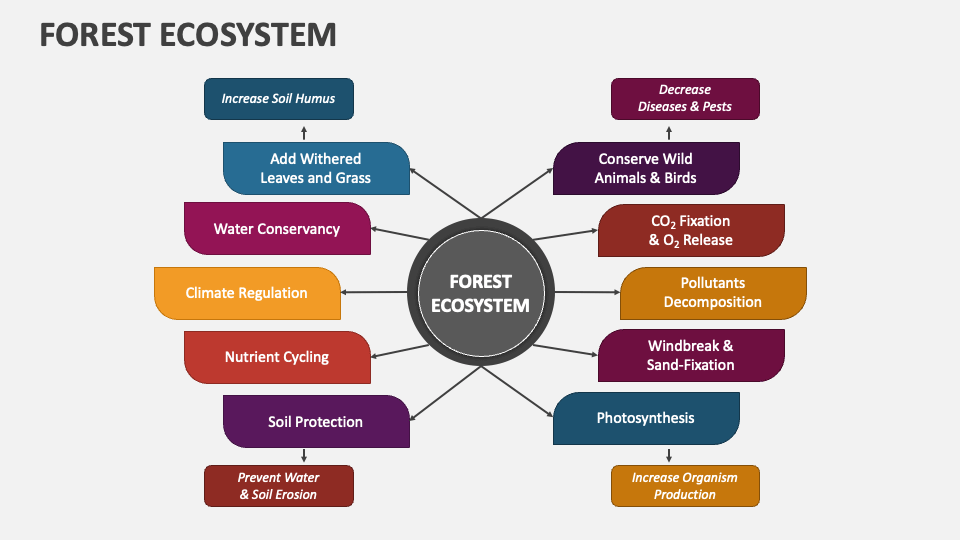
- Trees and Plants: Form the primary structure and provide oxygen.
- Animals and Insects: Depend on plants for food and shelter.
- Microorganisms: Decompose organic matter and recycle nutrients.
- Soil and Water: Support plant growth and maintain biodiversity.
4.What are the main layers of a forest?
Forests are divided into layers based on height:
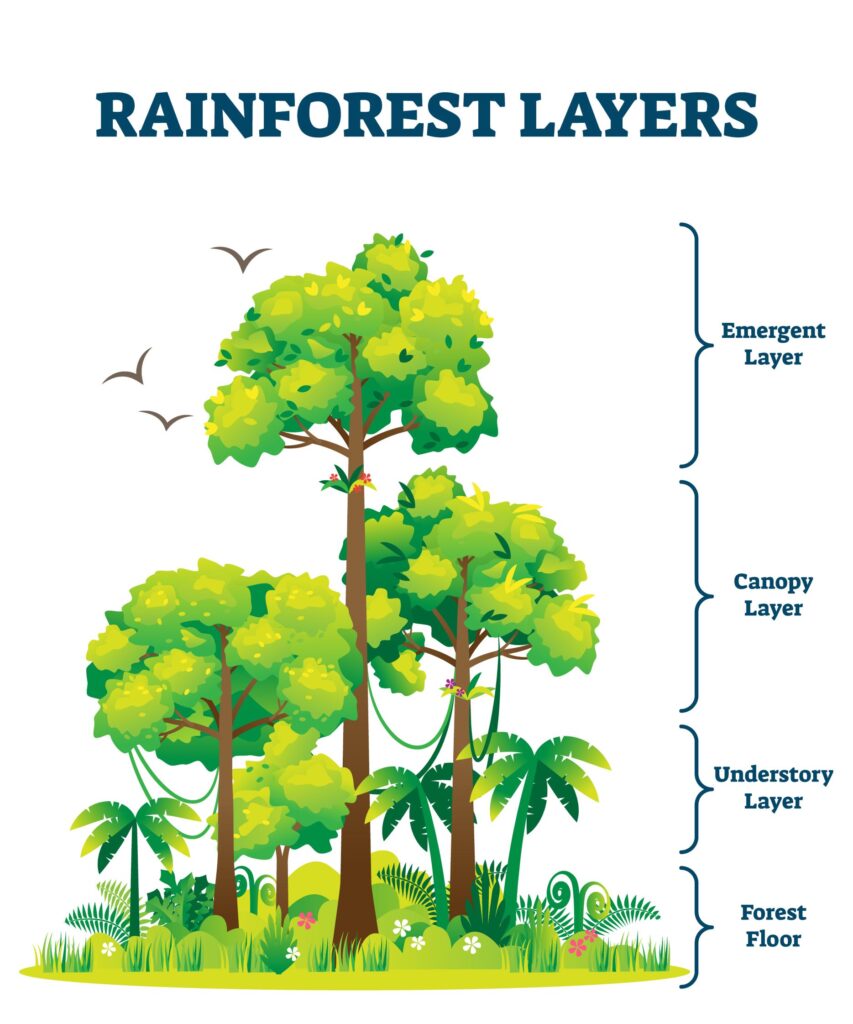
- Emergent Layer: Tallest trees that receive direct sunlight.
- Canopy Layer: Dense layer of tree branches that provide shelter for birds and insects.
- Understory Layer: Home to shrubs, small trees, and various animals.
- Forest Floor: Contains decomposed leaves, organic matter, and supports fungi, insects, and small mammals.
5. Why are forests called the ‘lungs of the Earth’?
Forests absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis, which helps in maintaining the atmospheric balance. This function is similar to how lungs purify air in the human body.
6. What are the major benefits of forests?
Forests provide numerous ecological, economic, and social benefits

- Oxygen Production: Essential for human and animal survival.
- Climate Regulation: Absorb CO₂, reducing global warming.
- Water Cycle Maintenance: Prevent soil erosion and increase groundwater levels.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Home to millions of species.
- Economic Resources: Timber, medicines, fruits, and more.
- Livelihood Support: Many indigenous communities depend on forests for survival.
7.What are the causes of deforestation?
Deforestation occurs due to:

- Agricultural Expansion: Clearing forests for farming and livestock.
- Urbanization: Land used for cities and infrastructure development.
- Logging Activities: Cutting trees for timber and paper industries.
- Mining and Industrialization: Extraction of minerals leads to habitat destruction.
- Natural Disasters: Wildfires, hurricanes, and floods also contribute.
8.What are the consequences of deforestation?

- Loss of Biodiversity: Destruction of animal and plant habitats.
- Climate Change: Increased CO₂ levels lead to global warming.
- Soil Erosion: Loss of fertile soil, reducing agricultural productivity.
- Water Cycle Disruption: Reduced rainfall and water scarcity.
- Livelihood Impact: Affects indigenous communities and forest dependent people.
9. What are the different methods of forest conservation?
- Afforestation and Reforestation: Planting new trees to restore forest cover.
- Sustainable Logging Practices: Controlled and responsible tree-cutting methods.
- Wildlife Protection Measures: Establishing national parks and reserves.
- Community Participation: Encouraging local communities in conservation efforts.
- Government Policies: Enforcing strict laws against illegal deforestation.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating people about the importance of forests.
10. How do forests help in preventing soil erosion?
Forests prevent soil erosion by:
- Holding soil with tree roots.
- Reducing the impact of heavy rainfall.
- Providing ground cover that stabilizes the soil.
11. How can individuals contribute to forest conservation?
Individuals can:
- Plant trees in their communities.
- Use recycled paper and sustainable wood products.
- Reduce wastage of forest resources.
- Support organizations working for forest conservation.
- Raise awareness about the impact of deforestation.
12. What is the role of forests in the water cycle?
Forests play a vital role in the water cycle by
- Absorbing rainwater and maintaining groundwater levels.
- Regulating river flow and preventing floods.
- Enhancing evaporation and rainfall patterns.
13. How do forests support biodiversity?
Forests provide:
- Shelter and food for diverse species.
- A breeding ground for animals and birds.
- Protection for endangered species.
14. What is sustainable forestry?
Sustainable forestry is the practice of managing forest resources responsibly to meet current needs while ensuring future generations can also benefit. This includes:
- Selective logging instead of clear-cutting.
- Promoting biodiversity-friendly practices.
- Restoring damaged ecosystems.
15. What are some famous forests around the world?
- Amazon Rainforest (South America): Largest tropical rainforest.
- Black Forest (Germany): Known for its dense trees and folklore.
- Congo Rainforest (Africa): Second-largest tropical rainforest.
- Daintree Rainforest (Australia): Home to unique flora and fauna.
Conclusion
Forests are an invaluable part of our planet, providing life-sustaining benefits. Conservation and sustainable management are essential to protect these ecosystems from destruction. Small efforts by individuals and communities can lead to a significant positive impact on forest preservation.
Useful links: