Class 7 Electric current and its effects
Questions Included are:
1. Define Electrical energy?
2. What are the elements of electric circuit ?
3. What are the various electrical components ?
4. What are symbols used for electrical components?
5. Define Electric cell?
6. Define Electric battery?
7. Difference between Electric cell and Battery?
8. Describe How cells are arranged in TV Remote control?
9. What are Storage cells ?
10.Define Electric circuit ?
11. Difference between open and closed circuit?
12. Define circuit diagram??
13. Define resistance?
14.Difference between Conductors and Insulators?
15. What are the three effects of electric current?
16. Define Heating effect of electric current?
17. What are the factors affecting heating effect of electric current?
18. what are the applications of Heating effect of electric current?
19. Describe in detail how the heating effect of electric current is used in electrical appliances?
20. How do Electric Bulb glow ?
21. Alternatives of Electric Bulb?
22. Define Electric fuse?
23. How does electric fuse work ?
24. What are MCB?
25.What are the causes of excessive Flow of current?
26. Define Magnetic effect of electric current ?
27. What is a solenoid?
28. Define Electromagnet?
29. How can the strength of electromagnet can be increased?
30. What are advantages of electromagnet over permanent magnet?
31. What are the uses of Electromagnets ?
32. Explain the construction of electric Bell ?
********************************************************
1. Define Electrical energy?
- Electricity provides a form of energy called Electrical energy.
- Electricity is used in lighting tubes, bulbs, fans, electrical appliances etc.
2. What are the elements of electric circuit ?
The components such as cell, bulbs, wires used in electrical circuit are called elements of electric circuit.
3. What are the various electrical components ?
Electric cell, Electric bulb, switch in ‘ON’ position, switch in ‘off’ position, Battery, wire, wires crossing without being connected, wires connected together, fixed resistance.
4. What are symbols used for electrical components?
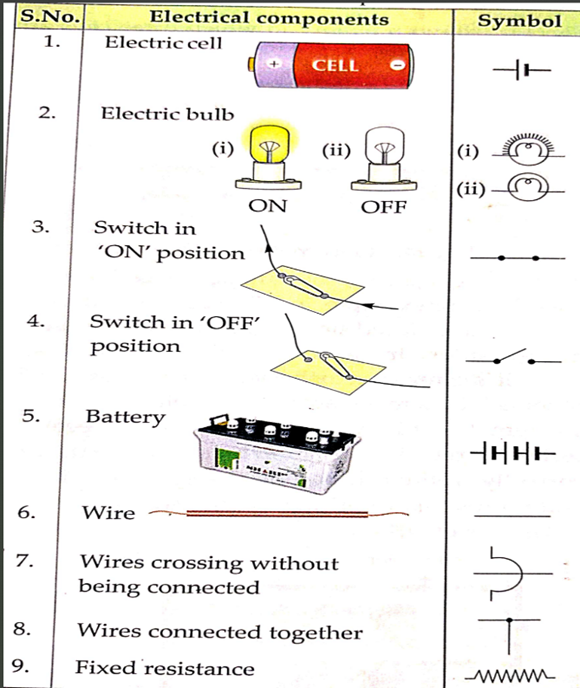
5. Define Electric cell?
- An electric cell is source of electric current used to run various electrical appliances such as torch, transistor, TV remote, watch, electronic toys etc.
- Every electric cell has a positive and negative terminal.
6. Define Electric battery?
- The combination of two or more cells is called battery.
- In a battery, electric cells can be connected in series or parallel.
- Electric battery are used in car, buses, tricks, tractor, invertors etc.
7. Difference between Electric cell and Battery?
| Feature | Electric Cell | Battery |
| Definition | A single unit that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. | A combination of two or more electric cells connected together. |
| Components | Contains two electrodes (positive and negative) and an electrolyte. | Consists of multiple electric cells connected in series or parallel. |
| Voltage | Provides a small voltage (usually 1.5V for a dry cell). | Provides a higher voltage depending on the number of cells used. |
| Usage | Used in small devices like torches, clocks, and remote controls. | Used in high-power devices like cars, laptops, and inverters. |
| Example | Dry cell, button cell. | Car battery, mobile phone battery. |
8. Describe How cells are arranged in TV Remote control?
- In TV Remote control, 2 cells are placed side by side in a cell holder to make battery
- 2. Positive terminal of one cell is connected to negative terminal of other cell by a metal strip in the cell holder of remote.
- 3. So cells are arranged in series.
- 4. The symbols ”+” and ”_” are printed on two sides of cell holder.
9. What are Storage cells ?
- Batteries used in car, bus, truck, inverters are made by connecting cells.
- A cut out of car battery having six cells are called as storage cells.
- These cells can be recharged, once exhausted they should be properly disposed off
10.Define Electric circuit ?
- The flow of electrons is called Electric current.
- Electric current flows from positive terminal of battery to negative terminal
- The path along which the electric current can flow is called electric circuit.
- The components of electric circuit are
- source of electric current = cell/ Battery
- conducting wire – copper wire
- Electric appliance – Bulb
- Switch – Key
11. Difference between open and closed circuit?
| Open circuit | Closed circuit |
| The electric path that starts from positive terminal of cell and broken at some point is called open circuit | The electric path that starts from positive terminal of cell ends at negative terminal without any break is called closed circuit |
| It is also called as Incomplete electric circuit No current flow in this circuit | It is also called as complete electric circuit Current flows in this circuit |
12. Define circuit diagram??
A diagram which shows the arrangement of various electrical component in an electric circuit with the help of their symbols is called circuit diagram.
13. Define resistance?
- The property of material by the virtue of which it opposes the flow of electric current through it is called resistance
- Lower the resistance, higher the current flows
14.Difference between Conductors and Insulators?
| Conductors | Insulators |
| The materials that allow current to pass through them are called as conductors. | The materials that do not allow current to pass through them are called as insulators |
| They are good conductors of electricity | They are bad conductors of electricity |
| They have low resistance | They have high resistance |
| Ex: Metals | Ex: Wood, Plastic, Rubber, Mica |
15. What are the three effects of electric current?
- Heating effect
- Magnetic effect
- Chemical effect
16. Define Heating effect of electric current?
- When an electric current passes through high resistance if wire (Nichrome) electrical energy is converted to heat energy that heats up the resistance wire.
- This is called Heating effect of electric current
17. What are the factors affecting heating effect of electric current?
- Resistance of material
- Magnitude of current passed through wire
Resistance of material:
- The higher resistance of material – Greater the heat produced
- Lower the resistance of material – Lesser the heat produced
Magnitude of current:
Greater the magnitude of current passed through wire, greater will be the heat produced.
18. what are the applications of Heating effect of electric current?
Heating effect of electric current is used in
- Electric heating appliances such as Electric Kettle, Electric Toaster etc
- Electric Bulb
- Electric Fuse
19. Describe in detail how the heating effect of electric current is used in electrical appliances?
- All the electric heating appliances contain a coil of high resistance wire called Heating element
- The high resistance wire is made up of Nichrome Iron, Nickel, chromium and Magnesium,
- When electric current is passed through electric heating appliance, large amount of heat is produced in element so it becomes red hot.
- Then it is used for desired application.Ex: Electric iron box – used to iron clothes
- OTG Oven = cook and bake food items.
20. How do Electric Bulb glow ?
- Electric Bulb works on the principle of heating effect of electric current.
- It has very thin, high resistance filament of Tungsten metal.
- When electric current is passed through tungsten filament, it becomes white hot and glowing
21. Alternatives of Electric Bulb?
- Electric Bulb gives out heat that leads to wastage of electricity.
- Hence they are replaced with LED’s and CFL’s.
- LED – Light Emitting Diode.
- CFL= Compact Fluorescent lamps.
- These are power efficient, long lasting, less electricity. They can be fixed in ordinary bulb holders.
- Before Buying any electrical appliance, ensure that it has ISI mark [Indian Standard Institute).
- ISI ensure that appliance is safe and wastage of energy is minimum.
22. Define Electric fuse?
- An electric fuse is a safety device that breaks the electric circuit when there is excessive flow of current in the circuit
- It prevents the damage to electrical appliance and fire.
- It works on the principle of heating effect of electric current.
23. How does electric fuse work ?
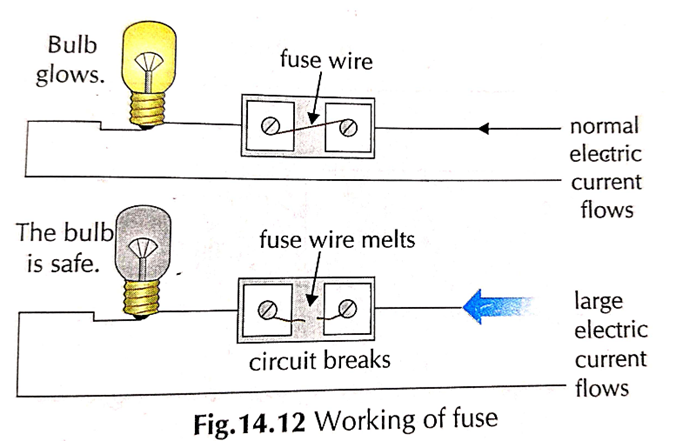
- A fuse consist of piece of thin wire (an alloy of tin and copper) having low point.
- It is always connected in series with electric circuit
- when excessive current flows in circuit, thin fuse wire gets too much heated, melts and break the circuit.
- Current stop flowing in circuit and prevent the damage of electrical appliance.
- when fuse gets melted, new fuse has to be fitted in the place to replace / restore the electric supply again in household circuit
24. What are MCB?
- MCB are Miniature circuit Breaker.
- These are switches that automatically turns off when current flow increases / overflow.
- When the fault is corrected, MCB can be reset to “on” position, and the circuit is complete again.
25.What are the causes of excessive Flow of current?
There are two main causes for the excessive flow of current
- Short circuit
- Overloading
Short circuit:
- We use cables and wires in electric circuit
- Wire consist of live wire, Neutral wire, Earth wire.
- A sudden flow of very large current due to direct contact of live and neutral wire is called as short circuit.
- Short circuit can also leads to fire.
Overloading:
- When many electrical appliances are connected in a single socket, there can be large inflow of cures
- The overheating of electrical wring in any circuit due to flow of large current through it is called overloading of electrical circuit.
26. Define Magnetic effect of electric current ?
- when electric current passes through a wire, the current carrying wire behaves like Magnet and produces Magnetic field around it. It is called Magnetic effect of electric current.
- It is first observed by Hans Christian oersted.
27. What is a solenoid?
- Cylindrical coil of wire is called Solenoid
- When current passes through solenoid, it behaves as a bar Magnet.
28. Define Electromagnet?
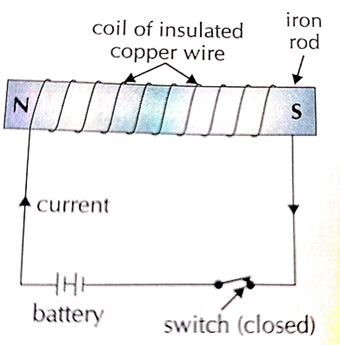
- Magnet produced by passing an electric current through coil of insulated wire wound around soft iron rod is called electromagnet.
- Magnetism of electromagnet last only till the current passes through the coil.
29. How can the strength of electromagnet can be increased?
The strength of electromagnet can be increased by
1.Increasing the number of turns in the coil
2. Increasing the current passing through Solenoid.
30. What are advantages of electromagnet over permanent magnet?
- Magnetism of electromagnet can be Switched “ON” or “off” as desired. This is not possible with permanent magnet
- Electromagnet can be made strong by increasing both the number of turns and amount of current passing through it. This is not possible with permanent magnet.
31. What are the uses of Electromagnets ?
- Electromagnets are used in Motors, fans, mixed, washing machine etc.
- Cranes with strong electromagnet are used to lift heavy loads like big machine, scrap Iron objects for loading & unloading purpose.
- Electromagnets are used to separate magnetic materials like Iron & Steel objects from metal scrap junk.
- Electromagnets are used by doctors to remove tiny iron particles from eyes of patient which may have fallen accidentantly.
- Electromagnets are used in electric bells, telegraph, telephone
Instruments , loudspeakers etc.
32. Explain the construction of electric Bell ?
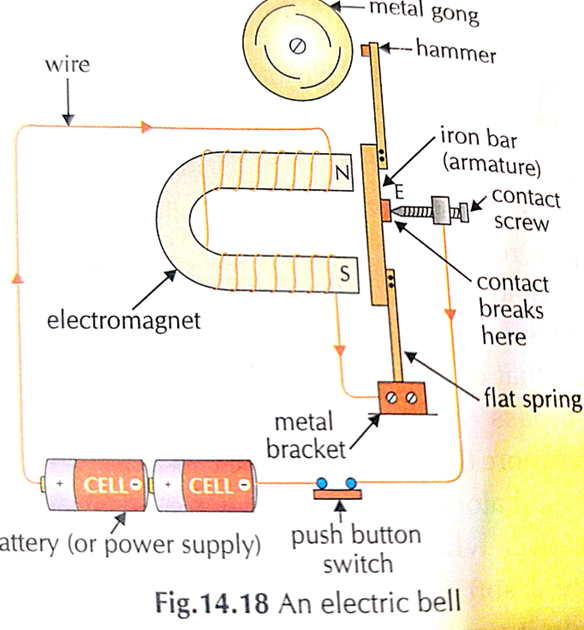
- An electric bell has Ushape electro magnet.
- Small iron bar called “Armature” is held in front of poles.
- Lower end of the armature is attached to the flat spring. The spring is fixed to the metal bracket.
- Upper end of armature has hammer attached to it.
- There is a contact Screw that touches armature at point E
- Metal Gong is attached / fixed near hammer.
- Electromagnet is connected to battery, push button switch and armature in a circuit.
- How does electric Bell works?
- When switch is pressed, electric circuit is completed and current passes through coil of electromagnet.
- It get magnetised
- Electromagnet attract the armature towards itself. Hammer attached strikes the gong to produce sound.
- When armature move towards magnet, its contact with contact screw is broken at Point ‘E
- So circuit breaks, no current flow, so electromagnet loses its Magnetism and so armature is no longer attracted by it
- Spring brings back the armature to its original position and the hammer moves away from gong.
- When the armature comes back and touches the contact screw, circuit is complete and current start flowing.
- Electromagnet becomes magnetised. This process of “make and break” of electric circuit occurs, when we press the switch
- So, hammer strikes the gong rapidly and produce continous sound, bell as Ringing
Useful links:
