class 6 discovering the past
Class 6 Social studies, History
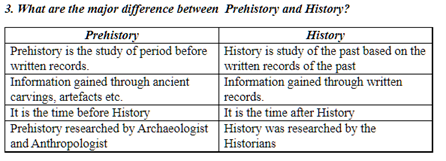
1. Define History?
· History means Study of Past.
· History is the study of Culture, life, tradition of different group of people who lived in different times.
· Parts of History are Science, Astronomy, Mathematics, Medicine.
2. Aryabhatta calculated the value of Pi (3.14) and length of the solar system
3. Varahamihira wrote book on astronomy
4. Sushrutha wrote book on Medicine and Surgery
5. Define Prehistory?
The period before history, when are not recorded and people do not know to read and write is called as Prehistory.
4. Why do we need to study about the History?
· History tells us about important events of past, changing human culture, beliefs, lifestyle, politics and much more.
· History helps us to connect the past to the present and built the future.
· History helps us to study the various styles and ideas of our ancient architects, engineers, sculptures, weavers, artist etc.
· History helps us to learn the rich cultural tradition followed by our ancestors.
· History helps the environmentalist to study the reason behind the depletion of natural resources over time and helps them to think about the remedial measures.
· Through History, we can have a broad vision and questioning mind of various topics like Economy, Education, Politics, Society and much more.
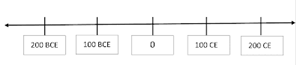
5. Define Timeline?
A chronological way of arranging events and instance in order of their occurrence is called as Timeline
Note:
BCE — Before Common Era
CE — Common Era
Decade — A period of 10 years
Century — A period of 100 years
Millennium — A period of 1000 years
First century started from 1st January 1 CE and ended in 31st December 100 CE.
Ex: 15th Century period is from 1401 CE — 1500 CE
At present we are in 21st century, it started in 2000s
5. What are the main sources to study about the past?
The two main sources to study about the past is Literary sources. Archaeological sources.
6. Define Archaeology?
· The study of History and prehistory through the excavation of sites and analysis of artefacts and other physical remains such as fossils etc is called as Archaeology.
· The person who studies about the archaeology is called as Archaeologist.
· They used tools like pick, shovels, spoon, brush and sometimes bulldozer to excavate a site.
7. How Archaeology helps to study about the past?
· Archaeologist study material remain from the past through the fossils, burial sites, artefacts, relics, weapons through the process of excavation.
· Using archaeological findings, archaeologist reconstruct the past by finding how old they are, what type of material was used to make these types of objects.
· Archaeological resources include mainly the artefacts, monuments, coins, inscriptions, burial sites.
8. What are Monuments?
Monuments are built to honour the memory of person and to say about the historical/ political information to improve the location appearance.
9. What are Inscriptions?
· Inscriptions are important message/ records/ accounts of the kings.
· Inscriptions are engraved on hard surfaces like Pillars, Temple walls, Caves.
10. Describe about Coins?
· Coins belonging to various dynasty are discovered at various places.
· Gold, Silver and Copper coins are found.
· Coins with the King / God faces have been discovered.
11. Write a short note on Burial sites?
· Burial sites provide the rich source of information for archaeologist and Historians.
· In Some sites, along with Skeleton food remains and tools were discovered. This means that ancient people believed in life after death.
· Important site is Shanidar cave in Iraq.
12. Write about the Paintings and Sculptures?
· Paintings and Sculptures helps the archaeologist to study about the human civilization.
· Ex: Bhimbetka paintings share the early human daily life’s, hunting scenes and much more.
13. What are Manuscripts?
· The writings of early humans on palm leaf, bark of birch trees are known as Manuscripts.
· Manuscripts are mainly written in code signal/ code and the experts they decode these ancient text.
14. What are the Literary sources of History?
· Literary work includes mainly Religious, Secular Literature, Biographies, Traveller’s accounts, Chronicles.
· Literary sources of history may be religious or non-religious.
· Most of them are written in Sanskrit language.
Religious Works examples:
Epics — Ramayana, Mahabharata
Scriptures — Vedas
Buddhist Literature — Jataka tales.
Non religious works:
Kautilya`s — Arthashastra
Kalidasa — Abhijinanashakuntalum
Banabhatta`s — Harsha Charita
Vishnu Sharma — Panchatantra
15. What is the correlation between the History and Geography?
· History helps to study about the Human experience and development and Geography focuses on how humans relate with the physical environment.
· Harappan civilisation developed near the banks of rivers. Most of the civilisation were developed near the banks of river since early humans were nomads and they settled near the river to get water and food.
· Through Khyber pass ( a mountain pass) an important trade route was developed connecting the Afghanistan and Pakistan. It was the main way of foreign invasion for Alexander The Great and Genghis Khan.